Has Exponented factors & an exponent. More...
Public Member Functions | |
| def | __init__ |
| Constructor. | |
| def | get_factors_list_except |
| Returns the factors' list of the Product except the given one. | |
| def | get_first_factor |
| Returns the first Sum/Item factor of the Product. | |
| def | get_minus_signs_nb |
| Returns the number of - signs (negative factors) in the Product. | |
| def | get_factors_list |
| Returns the factors' list of a given kind (numeric, literal...) For instance, for the product : 2x × (-4x²) × (x + 3)³ × 5 × (x²)³ × (-1)² × (2×3)², this method would return : | |
| def | set_factor |
| def | into_str |
| Creates a string of the given object in the given ML. | |
| def | calculate_next_step |
| Returns the next calculated step of a numeric Product. | |
| def | expand_and_reduce_next_step |
| Returns the next step of reduction of the Product It won't check if it is expandable. | |
| def | __cmp__ |
| Compares two Products Returns 0 if all factors are the same in the same order and if the exponents are also the same /!\ a × b will be different from b × a It's not a mathematical comparison, but a "displayable"'s one. | |
| def | operator |
| Defines the performed CommutativeOperation as a Product. | |
| def | multiply_symbol_is_required |
| True if the usual writing rules require a × between two factors. | |
| def | requires_brackets |
| True if (one)self requires brackets inside of a Product. | |
| def | requires_inner_brackets |
| True if the argument requires inner brackets The reason for requiring them is having an exponent different from 1 and several terms or factors (in the case of Products & Sums) | |
| def | order |
| Returns the Product once put in order. | |
| def | reduce_ |
| Return a reduced Product (if possible) For instance, giving this Product : 2x × (-4x²) × (x + 3)³ × 5 × (x²)³ × (-1)² × (2×3)², reduce_() would return : | |
| def | is_null |
| True if any of the factors is null. | |
| def | is_displ_as_a_single_1 |
| True if the Product contains only single 1s. | |
| def | is_displ_as_a_single_minus_1 |
| True if the Product can be displayed as a single -1 For instance, the Product 1×1×(-1)×1. | |
| def | is_displ_as_a_single_0 |
| True if the object can be DISPLAYED as a single 0 For instance, the Product 0×0×0×0 (but NOT 0×1) | |
| def | is_reducible |
| True if the Product is reducible This is based on the result of the get_factors_list method. | |
Public Attributes | |
| str_openmark | |
| str_closemark | |
Properties | |
| factor | |
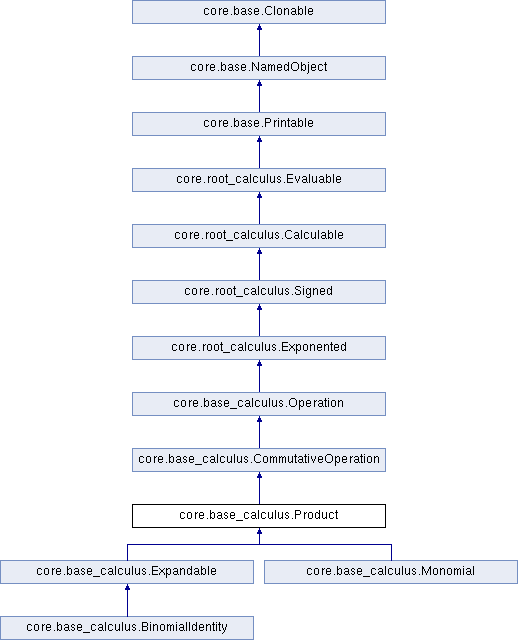
Detailed Description
Has Exponented factors & an exponent.
Iterable. Two display modes.
Definition at line 4130 of file base_calculus.py.
Constructor & Destructor Documentation
| def core.base_calculus.Product.__init__ | ( | self, | |
| arg | |||
| ) |
Constructor.
- Warning:
- Might raise an UncompatibleType exception.
- Parameters:
-
arg None|Product|Number|Exponented|[Numbers|Exponenteds] In the case of the list, the Products having an exponant equal to 1 won't be treated so that their factors are inserted in the current Product instead of inserting a factor as a Product. If it would, then the compact and non compact display properties might be lost. (For instance, multiplying two Monomials and setting the compact display field of the resulting Product to False would result in displaying all the Monomials Items which isn't always wished) If the argument isn't of the kinds listed above, an exception will be raised. Giving None or an empty list is equivalent to giving 1. The exponent of a Product is 'outside' (like 3 in (4×5x)³)
- Returns:
- An instance of Product
Definition at line 4153 of file base_calculus.py.
References core.base_calculus.CommutativeOperation._compact_display, core.base_calculus.Product._compact_display, core.base_calculus.Item._exponent, core.base_calculus.Function._exponent, core.base_calculus.Quotient._exponent, core.base_calculus.Fraction._exponent, core.base_calculus.Product._exponent, core.base_calculus.Operation._neutral, core.base_calculus.Product._neutral, core.base_calculus.Operation._symbol, core.base_calculus.Quotient._symbol, core.base_calculus.Fraction._symbol, core.base_calculus.Product._symbol, core.base.Clonable.clone(), core.base_calculus.CommutativeOperation.str_closemark, core.base_calculus.Product.str_closemark, core.base_calculus.CommutativeOperation.str_openmark, and core.base_calculus.Product.str_openmark.
Referenced by core.calculus.Equation.__init__(), and core.root_calculus.Value.substitute().
Member Function Documentation
| def core.base_calculus.Product.__cmp__ | ( | self, | |
| objct | |||
| ) |
Compares two Products Returns 0 if all factors are the same in the same order and if the exponents are also the same /!\ a × b will be different from b × a It's not a mathematical comparison, but a "displayable"'s one.
- Returns:
- 0 if all factors are the same in the same order & the exponent
Definition at line 5468 of file base_calculus.py.
References core.base_calculus.Item.exponent, core.root_calculus.Exponented.exponent, core.base_calculus.Fraction.exponent, and core.base_calculus.Product.factor.
| def core.base_calculus.Product.calculate_next_step | ( | self, | |
| options | |||
| ) |
Returns the next calculated step of a numeric Product.
- Todo:
This method is only very partially implemented (see source code)
The way the exponents are handled is still to be decided
the inner '-' signs (±(-2)) are not handled by this method so far
Reimplemented from core.root_calculus.Calculable.
Definition at line 5110 of file base_calculus.py.
References core.base_calculus.CommutativeOperation.compact_display, core.root_calculus.Evaluable.evaluate(), core.base_calculus.Item.evaluate(), core.root_calculus.Value.evaluate(), core.base_calculus.Quotient.evaluate(), core.base_calculus.Fraction.evaluate(), core.base_calculus.CommutativeOperation.evaluate(), core.base_calculus.Item.expand_and_reduce_next_step(), core.base_calculus.SquareRoot.expand_and_reduce_next_step(), core.base_calculus.Fraction.expand_and_reduce_next_step(), core.base_calculus.Product.expand_and_reduce_next_step(), core.base_calculus.Item.exponent, core.root_calculus.Exponented.exponent, core.base_calculus.Fraction.exponent, core.base_calculus.Product.factor, core.base_calculus.Product.is_displ_as_a_single_1(), core.base_calculus.Product.is_displ_as_a_single_minus_1(), core.root_calculus.Evaluable.is_numeric(), core.base_calculus.Item.is_numeric(), core.root_calculus.Value.is_numeric(), core.base_calculus.SquareRoot.is_numeric(), core.base_calculus.Operation.is_numeric(), core.calculus.Table.is_numeric(), and core.base_calculus.Monomial.is_numeric().
Referenced by core.base_calculus.CommutativeOperation.evaluate(), core.base_calculus.Product.expand_and_reduce_next_step(), and core.base_calculus.Sum.expand_and_reduce_next_step().
| def core.base_calculus.Product.expand_and_reduce_next_step | ( | self, | |
| options | |||
| ) |
Returns the next step of reduction of the Product It won't check if it is expandable.
Either it IS and the object is not just a Product but an Expandable or it isn't.
- Returns:
- Exponented
Reimplemented from core.root_calculus.Calculable.
Reimplemented in core.base_calculus.BinomialIdentity, and core.base_calculus.Expandable.
Definition at line 5361 of file base_calculus.py.
References core.base_calculus.Item.calculate_next_step(), core.base_calculus.SquareRoot.calculate_next_step(), core.base_calculus.Quotient.calculate_next_step(), core.base_calculus.Fraction.calculate_next_step(), core.base_calculus.Product.calculate_next_step(), core.base_calculus.Item.dbg_str(), core.root_calculus.Value.dbg_str(), core.calculus.Equation.dbg_str(), core.base_calculus.SquareRoot.dbg_str(), core.base_calculus.Quotient.dbg_str(), core.base_calculus.Fraction.dbg_str(), core.base_calculus.CommutativeOperation.dbg_str(), core.base_calculus.Monomial.dbg_str(), core.base_calculus.Polynomial.dbg_str(), core.base_calculus.Expandable.expand(), core.base_calculus.BinomialIdentity.expand(), core.base_calculus.Product.get_first_factor(), core.base_calculus.Product.is_displ_as_a_single_minus_1(), core.root_calculus.Evaluable.is_numeric(), core.base_calculus.Item.is_numeric(), core.root_calculus.Value.is_numeric(), core.base_calculus.SquareRoot.is_numeric(), core.base_calculus.Operation.is_numeric(), core.calculus.Table.is_numeric(), core.base_calculus.Monomial.is_numeric(), core.root_calculus.Signed.is_positive(), core.base_calculus.Fraction.is_reducible(), core.base_calculus.Product.is_reducible(), and core.base_calculus.Product.reduce_().
Referenced by core.base_calculus.Product.calculate_next_step(), and core.base_calculus.Sum.calculate_next_step().
| def core.base_calculus.Product.get_factors_list | ( | self, | |
| given_kind | |||
| ) |
Returns the factors' list of a given kind (numeric, literal...) For instance, for the product : 2x × (-4x²) × (x + 3)³ × 5 × (x²)³ × (-1)² × (2×3)², this method would return :
- in the case of simple numeric items : [2, -4, 5, (-1)², 2², 3²]
- in the case of simple literal items : [x, x², x**6]
- in the "others" list : [(x+3)³] This method helps to reduce a Product. It doesn't calculate anything and doesn't manage exotic cases (imbricated Products...) which are too complex to foresee. As far as I could... (later note : but I'm not sure it doesn't manage them now, I might have done that later than this comment). It will still be convenient to reorder the factors of a Monomials Product.
- Parameters:
-
given_kind : NUMERIC | LITERALS | OTHERS
- Returns:
- a list containing the factors
- Todo:
- The - signs of the literals should be treated as -1 in the numeric list (and shouldn't remain in the literals' list)
Definition at line 4332 of file base_calculus.py.
References core.base_calculus.CommutativeOperation.compact_display, core.base_calculus.Item.dbg_str(), core.root_calculus.Value.dbg_str(), core.calculus.Equation.dbg_str(), core.base_calculus.SquareRoot.dbg_str(), core.base_calculus.Quotient.dbg_str(), core.base_calculus.Fraction.dbg_str(), core.base_calculus.CommutativeOperation.dbg_str(), core.base_calculus.Monomial.dbg_str(), core.base_calculus.Polynomial.dbg_str(), core.base_calculus.Operation.element, core.base_calculus.Item.exponent, core.root_calculus.Exponented.exponent, and core.base_calculus.Fraction.exponent.
Referenced by core.base_calculus.Product.is_reducible(), core.base_calculus.Product.order(), and core.base_calculus.Product.reduce_().
| def core.base_calculus.Product.get_first_factor | ( | self | ) |
Returns the first Sum/Item factor of the Product.
- Warning:
- Maybe not functionnal because of the 1's... For instance, if <factor1,factor2> is a Product & [term1,term2] a Sum: <<2,3>,x> would return 2 <[2,3],x>² would return (2+3)² <<2x>²,4> would return 2²
- Todo:
- check the intricate case of <<[<0, 1>]>, 4>
Definition at line 4271 of file base_calculus.py.
References core.base_calculus.Item.exponent, core.root_calculus.Exponented.exponent, core.base_calculus.Fraction.exponent, and core.base_calculus.Product.factor.
Referenced by core.base_calculus.Product.expand_and_reduce_next_step().
| def core.base_calculus.Product.into_str | ( | self, | |
| options | |||
| ) |
Creates a string of the given object in the given ML.
- Parameters:
-
options Any options
- Returns:
- The formated string
Reimplemented from core.base.Printable.
Reimplemented in core.base_calculus.BinomialIdentity.
Definition at line 4514 of file base_calculus.py.
References core.base_calculus.CommutativeOperation.compact_display, core.base_calculus.Item.dbg_str(), core.root_calculus.Value.dbg_str(), core.calculus.Equation.dbg_str(), core.base_calculus.SquareRoot.dbg_str(), core.base_calculus.Quotient.dbg_str(), core.base_calculus.Fraction.dbg_str(), core.base_calculus.CommutativeOperation.dbg_str(), core.base_calculus.Monomial.dbg_str(), core.base_calculus.Polynomial.dbg_str(), core.root_calculus.Exponented.exponent_must_be_displayed(), core.base_calculus.Product.factor, core.base_calculus.Product.get_factors_list_except(), core.base_calculus.CommutativeOperation.info, core.base_calculus.Product.is_displ_as_a_single_1(), core.base_calculus.Product.is_displ_as_a_single_minus_1(), core.base_calculus.Product.multiply_symbol_is_required(), core.base_calculus.Product.requires_brackets(), core.base_calculus.Item.requires_inner_brackets(), core.base_calculus.SquareRoot.requires_inner_brackets(), core.base_calculus.Quotient.requires_inner_brackets(), and core.base_calculus.Product.requires_inner_brackets().
True if the Product contains only single 1s.
For instance, 1×1×1
Reimplemented from core.root_calculus.Calculable.
Definition at line 5710 of file base_calculus.py.
References core.base_calculus.Product.factor, core.root_calculus.Calculable.is_displ_as_a_single_neutral(), core.base_calculus.Item.is_displ_as_a_single_neutral(), core.base_calculus.SquareRoot.is_displ_as_a_single_neutral(), core.base_calculus.Quotient.is_displ_as_a_single_neutral(), and core.base_calculus.CommutativeOperation.is_displ_as_a_single_neutral().
Referenced by core.base_calculus.Expandable.__init__(), core.base_calculus.Product.calculate_next_step(), core.base_calculus.Expandable.expand(), core.base_calculus.Expandable.expand_and_reduce_next_step(), core.base_calculus.Product.into_str(), core.base_calculus.Product.is_reducible(), core.base_calculus.Sum.is_reducible(), and core.base_calculus.Sum.requires_inner_brackets().
| def core.base_calculus.Product.is_reducible | ( | self | ) |
True if the Product is reducible This is based on the result of the get_factors_list method.
- Returns:
- True|False
- Todo:
- check the comment in the code Fix the problem bound to the get_factors list not giving - signs of literals as -1 in the list of numerics.
Definition at line 5778 of file base_calculus.py.
References core.base_calculus.CommutativeOperation.compact_display, core.base_calculus.CommutativeOperation.dbg_str(), core.base_calculus.Product.get_factors_list(), core.base_calculus.Item.is_displ_as_a_single_0(), core.base_calculus.Function.is_displ_as_a_single_0(), core.base_calculus.SquareRoot.is_displ_as_a_single_0(), core.base_calculus.Quotient.is_displ_as_a_single_0(), core.base_calculus.Product.is_displ_as_a_single_0(), core.base_calculus.Item.is_displ_as_a_single_1(), core.base_calculus.Function.is_displ_as_a_single_1(), core.base_calculus.SquareRoot.is_displ_as_a_single_1(), core.base_calculus.Quotient.is_displ_as_a_single_1(), core.base_calculus.Product.is_displ_as_a_single_1(), core.base_calculus.Item.is_displ_as_a_single_minus_1(), core.base_calculus.Function.is_displ_as_a_single_minus_1(), core.base_calculus.SquareRoot.is_displ_as_a_single_minus_1(), core.base_calculus.Quotient.is_displ_as_a_single_minus_1(), core.base_calculus.Product.is_displ_as_a_single_minus_1(), core.base_calculus.Operation.is_literal(), core.base_calculus.Operation.is_numeric(), and core.base_calculus.CommutativeOperation.throw_away_the_neutrals().
Referenced by core.base_calculus.Product.expand_and_reduce_next_step().
| def core.base_calculus.Product.multiply_symbol_is_required | ( | self, | |
| objct, | |||
| position | |||
| ) |
True if the usual writing rules require a × between two factors.
- Parameters:
-
objct The other one position The position (integer) of self in the Product
- Todo:
- check Why in source code
- Returns:
- True if the writing rules require × between self & obj
Reimplemented from core.root_calculus.Calculable.
Definition at line 5505 of file base_calculus.py.
References core.base_calculus.Product.factor, core.base_calculus.Item.multiply_symbol_is_required(), core.base_calculus.SquareRoot.multiply_symbol_is_required(), core.base_calculus.Quotient.multiply_symbol_is_required(), and core.base_calculus.Product.multiply_symbol_is_required().
Referenced by core.base_calculus.Product.into_str(), core.base_calculus.Product.multiply_symbol_is_required(), and core.base_calculus.Sum.multiply_symbol_is_required().
| def core.base_calculus.Product.reduce_ | ( | self | ) |
Return a reduced Product (if possible) For instance, giving this Product : 2x × (-4x²) × (x + 3)³ × 5 × (x²)³ × (-1)² × (2×3)², reduce_() would return :
-1440 * x⁹ * (x + 3)³
Definition at line 5649 of file base_calculus.py.
References core.base_calculus.Item.dbg_str(), core.root_calculus.Value.dbg_str(), core.calculus.Equation.dbg_str(), core.base_calculus.SquareRoot.dbg_str(), core.base_calculus.Quotient.dbg_str(), core.base_calculus.Fraction.dbg_str(), core.base_calculus.CommutativeOperation.dbg_str(), core.base_calculus.Monomial.dbg_str(), core.base_calculus.Polynomial.dbg_str(), core.base_calculus.CommutativeOperation.evaluate(), and core.base_calculus.Product.get_factors_list().
Referenced by core.base_calculus.BinomialIdentity.__init__(), core.base_calculus.Expandable.expand(), and core.base_calculus.Product.expand_and_reduce_next_step().
| def core.base_calculus.Product.requires_brackets | ( | self, | |
| position | |||
| ) |
True if (one)self requires brackets inside of a Product.
For instance, a Sum with several terms or a negative Item would.
- Parameters:
-
position The position of the object in the Product
- Returns:
- True if the object requires brackets in a Product
Reimplemented from core.root_calculus.Calculable.
Definition at line 5542 of file base_calculus.py.
References core.base_calculus.CommutativeOperation.throw_away_the_neutrals().
Referenced by core.base_calculus.Product.into_str().
True if the argument requires inner brackets The reason for requiring them is having an exponent different from 1 and several terms or factors (in the case of Products & Sums)
- Returns:
- True if the object requires inner brackets
Reimplemented from core.root_calculus.Calculable.
Definition at line 5581 of file base_calculus.py.
References core.root_calculus.Exponented.exponent_must_be_displayed().
Referenced by core.base_calculus.Product.into_str().
| def core.base_calculus.Product.set_factor | ( | self, | |
| n, | |||
| arg | |||
| ) |
- Parameters:
-
n : number of the factor to set arg : the object to put as n-th factor
Definition at line 4503 of file base_calculus.py.
References core.base_calculus.Operation.set_element().
Property Documentation
core::base_calculus.Product::factor [static] |
property(CommutativeOperation.get_element,
doc = "To access the factors of the Product.")
Definition at line 4491 of file base_calculus.py.
Referenced by core.base_calculus.Product.__cmp__(), core.base_calculus.Monomial.__init__(), core.base_calculus.Expandable.__init__(), core.base_calculus.Product.calculate_next_step(), core.base_calculus.Expandable.expand(), core.base_calculus.Expandable.expand_and_reduce_next_step(), core.base_calculus.Monomial.get_coeff(), core.base_calculus.Monomial.get_degree(), core.base_calculus.Product.get_factors_list_except(), core.base_calculus.Product.get_first_factor(), core.base_calculus.Monomial.get_first_letter(), core.base_calculus.Monomial.get_sign(), core.base_calculus.Product.into_str(), core.base_calculus.BinomialIdentity.into_str(), core.base_calculus.Product.is_displ_as_a_single_1(), core.base_calculus.Product.multiply_symbol_is_required(), and core.base_calculus.Monomial.set_degree().
The documentation for this class was generated from the following file:
- mathmaker_dev/core/base_calculus.py
 1.7.6.1
1.7.6.1